There are many engine-related problems. One such is your motorcycle engine running even after the ignition is turned off.
Using the kill switch doesn’t change things either.
So what causes the engine to run?
Here are the reasons why the motorcycle engine still runs even after the ignition is switched off:
- Pre-ignition due to hot spark plug
- Too lean air-fuel mixture
- Carbon deposits in the cylinder
- Damaged cylinder head gasket
- High compression ratio
The underlying issue in all of these causes is pre-ignition. The fuel mixture in the engine gets detonated without the need for spark ignition.
That’s why even after you turn the ignition switch off (which cuts off the spark), the fuel ignites. And hence the engine runs.
Let’s discuss each of these causes and their solutions in detail.
#1. Pre-ignition due to hot spark plug

Pre-ignition, in simple words, is when the engine ignites the fuel mixture even before the spark.
Usually, the spark is generated by the spark plug to ignite the fuel mixture. But in pre-ignition, the fuel mixture gets ignited without the spark.
That’s where the problem lies.
Even when you have you have turned the ignition switch off, which stops further sparks, the fuel mixture is ignited due to pre-ignition.
That’s why the engine still keeps running despite turning the ignition switch off.
So what causes pre-ignition?
Overheated spark plugs.
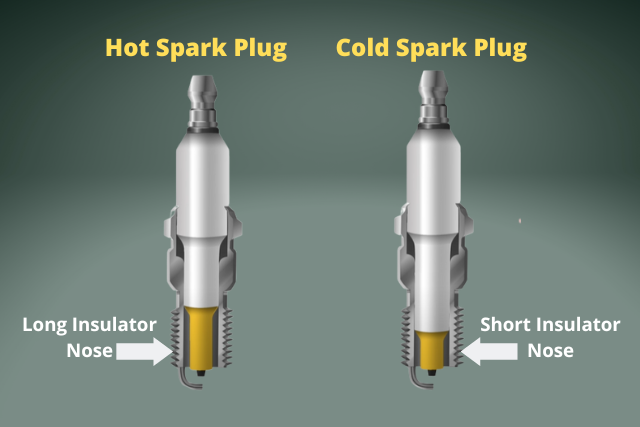
And overheated spark plugs are very common in engines using hot spark plugs.
Hot spark plugs have more insulation close to the tip which reduces heat transfer and maintains a high temperature in the tip.
So what’s the solution?
Solution:
The solution is to fit a colder spark plug.
Cold spark plugs have less insulation close to the tip, leading to more heat transferred away and reducing the tip temperature.
Colder spark plugs prevent pre-ignition in the engine.
But, on the flip side, the chances of carbon-fouling are more in cold spark plugs.
For a detailed comparison between hot vs cold spark plugs, you can check out our post here.
For the current engine problem, choose a colder spark plug than the one the engine is using.
How to know whether the spark plug is a cold or hot spark plug?
Hot spark plugs have longer insulator noses. So switch to a spark plug with a shorter insulator nose. That will give you a colder spark plug.
Once you have chosen a colder spark plug, replace it by taking out the current hot spark plug.
This should solve the pre-ignition problem and the motorcycle engine should stop igniting the fuel once the ignition switch is off.
#2. Too lean air-fuel mixture

A lean air-fuel mixture refers to more amounts of air present for the quantity of fuel in the air-fuel mixture.
In short, the fuel amount is low and the air is too much here.
A lean air-fuel mixture will have so much air that it causes too much heating in the engine.
The heat produced after combustion in the engine will not have sufficient exhaust gases to carry it. The air will be superheated and will eventually transfer the heat to the engine components.
As a result, the overheated engine components ignite the fuel mixture without the need for any spark.
Solution:
If the air-fuel mixture entering the engine is not right, then you need to tune the carburetor.
Whether the fuel mixture is lean or rich, an incorrect fuel mixture is not right for efficient combustion.
And in either case, the best solution is to tune the carburetor.
While detailing the carburetor tuning process is out of this post’s scope, here is a tuning video I really like.
#3. Carbon deposits in the cylinder

Next cause. The engine cylinder has too much carbon deposits.
Carbon deposits not only give uneven engine starts (won’t start when you want to, keeps running when you don’t want to) but also results in engine misfires, poor fuel economy, and black exhaust gases.
Most of the deposits are concentrated on top of the piston surface.
This in turn affects the engine compression ratio (which is another cause discussed below).
So, carbon deposits in the engine cylinder are a bad thing for a motorcycle. They need to be addressed.
Solution:
There are different ways to decarbonize depending on the amount of carbon deposits in the cylinder.

Let’s look at them starting from the easiest to the toughest:
- Gasoline additives: using gasoline additives to remove carbon deposits in the cylinder works great for recent and small carbon deposits. Decarbonizing and deposit control additives help in effectively removing these deposits.
- Cleaning intake valves: this is applicable especially for direction injection engines where gasoline is directly added to the combustion chamber. Cleaning intake valves help in mitigating carbon deposit formation in the cylinder.
- Chemical flushing: this is similar to gasoline additives except instead of adding additives to gasoline, the chemicals are directly flushed into the engine. These chemicals remove the carbon deposits. Seafoam treatment is particularly popular in this type of flushing.
- Taking the cylinder out and cleaning: this is the good old cleaning method. Use a scrubber, wire brush, and a cleaning agent. And brush the surface until you get rid of all the carbon deposits.
#4. Damaged cylinder head gasket

Another probable cause is to do with the cylinder head gasket.
The effects of the cylinder head gasket on the engine temperature is an established one. Anything wrong with the head gasket can lead to the engine and its parts overheating.
And an overheated engine leads to uneven fuel combustion. Also resulting in the engine igniting the fuel mixture even after the ignition is turned off.
The most probable issue is the cylinder head gasket projecting into the combustion chamber.
In such cases, the head gasket is damaged. Replacing the gasket is the only choice available.
Solution:
Cylinder gasket issues are tricky to inspect. Rather than adjusting the old cylinder gasket back in the right position, it is always better to replace it with a new gasket.
Again, replacing the cylinder gasket is easier said than done.

It is better to take your motorcycle to a service center and replace the head gasket there.
You can try doing-it-yourself too. But it’s going to be time-consuming and laborious process.
#5. High compression ratio

A high compression ratio in the engine is another cause of engine combustion even when the ignition is turned off.
The compression ratio is measured as the volume of the combustion chamber when the piston is at its lowest point (BDC – Bottom dead center) to when the volume when the piston is at its highest point (TDC – Top dead center).
In simple terms, the compression ratio is the ratio of the cylinder volume when it is highest to its lowest volume.
The compression ratios of motorcycle engines are usually between 8:1 to 13:1.
But if the compression ratio is on the higher side, there will be cases of engine knocking and pre-detonation.
The high compression coupled with a heated chamber ignites the fuel mixture without needing the spark ignition.
Solution:
Lowering the engine compression ratio is next to an impossible task without changing the engine or without affecting the engine working.
But there are 2 tricks that can be used. Of course, it doesn’t change the compression ratio drastically, but it will have a noticeable effect.
- Change the head gasket: using a thick cylinder gasket helps in lowering the compression ratio ever so slightly. But enough to cause a change in engine performance. This should suffice for the engine running problem even after the ignition is switched off.
- Change the piston: Aftermarket pistons are pretty cheap. To lower the compression ratio, use a hollow crown piston. The increased clearance volume helps in lowering the engine compression ratio.

To Summarize
To wrap up, here are the solutions when your motorcycle engine keeps running despite turning the ignition switch off:
- Solution 1: Change the hot spark plug. A hot spark plug cause pre-ignition in the engine. Switching to a colder spark plug prevents that.
- Solution 2: Tune the carburetor. Too lean air-fuel mixture pre-detonates without the need for spark ignition. Tune the carb for optimum air-fuel ratio.
- Solution 3: Decarbonize the cylinder. Carbon deposits in the cylinder are another problem. Decarbonize using additives, chemical flushing, or cleaning the intake valves.
- Solution 4: Change the head gasket. A damaged head gasket leads to heat spots, which leads to pre-detonation. So, replace the gasket with a new one.
- Solution 5: Lower the compression ratio. Either by shifting to a thicker head gasket or replacing the piston with a hollow crown or both.
