Engine compression ratios help the engine to achieve higher thermal efficiency. So for a motorcycle to perform well, engine compression ratio matters as well.
Then, what is a good compression ratio for a motorcycle? Since motorcycles use gasoline engines in them, the optimum compression ratio is between 8:1 to 13:1.
If the compression ratio is lower than optimum, there will be trouble in fuel combustion.
Similarly, if the compression ratio is too much, like that of diesel engines, then there will be engine knocking.
So motorcycles need to have desired compression ratio to operate and function well. Let’s dig deeper into the compression ratios and understand their significance more.
What is a compression ratio?

The compression ratio is measured as the volume of the combustion chamber when the piston is at its lowest point (BDC – Bottom dead center) to when the volume when the piston is at its highest point (TDC – Top dead center).
Too technical?
Let’s break this down one by one.
The piston moves to and from within the engine cylinder. When the piston moves down, the cylinder volume expands, and when the cylinder moves up, the cylinder volume contracts.
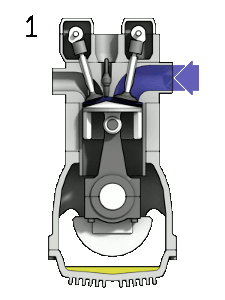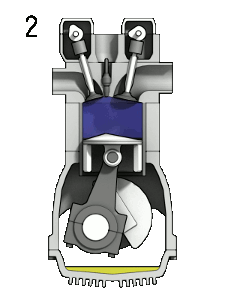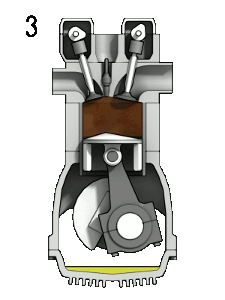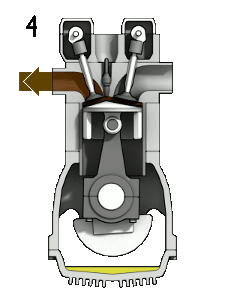
So, the cylinder volume is continuously expanding and contracting. And the piston is continuously moving up and down.
Now, when the piston reaches its lowest point of movement, it is called as Bottom dead center (BDC).
Similarly, when the piston reaches its highest point, it is called as Top dead center (TDC).
The piston moves up and down between the TDC and the BDC.
Next, when the piston is at BDC, the engine cylinder will have the largest volume. The piston is at its lowest point. The cylinder volume has expanded due to the piston down movement.
Similarly, when the piston is at TDC, the engine cylinder will have the lowest volume.
That’s enough basics. This should suffice to explain the compression ratio now.
The compression ratio measures how much of the cylinder volume does the piston compress.
And how do measure that?
By taking the ratio of the cylinder volume when it was highest to its lowest volume.
In other words, the compression ratio measures the cylinder volume when the piston is at BDC to the volume when the piston is at BDC.
Compression ratio of a gasoline engine

Gasoline engines are basically engines that use gasoline as fuel.
Now, why is the type of fuel such a big deal?
It is. That’s because the engine needs to ignite and burn the fuel. And different fuels have different ignition temperatures and conditions.
So based on the fuel, be it gasoline or diesel, the engine should have a customized design as well.
Gasoline engines are ignited by spark plugs. On the other hand, diesel engines are ignited by high compression. Also, diesel engines do not have spark plugs in them. Rather, they have glow plugs to heat the fuel mixture.
Now, enough of these design differences. What is the compression ratio of a gasoline engine?
The compression ratios of gasoline engines used in automobiles are usually between 8:1 to 13:1.
This compression ratio is lower when compared to that of diesel engines. This is because gasoline engines ignite the fuel mixture using spark ignition.
So, while the compression of the fuel mixture is important, it is not the igniting feature in gasoline engines.
Compression ratio of a diesel engine

Diesel engines, as discussed above, will typically have a high compression ratio.
The high compression ratio is necessary because diesel engines ignite the fuel mixture by compression.
The diesel fuel mixture gets ignited when highly compressed. Since the fuel is ignited by compression, diesel engines do not have spark plugs in them.
But, they do have glow plugs in them. The glow plug heats the diesel combustion chamber. This comes in handy whenever there are cold weather conditions outside and the engine is too cold to start with only the compression.
Typically, the compression ratios of diesel engines range between 14:1 to 23:1.
Diesel engines that use indirect fuel injection will have higher compression ratios starting from 18:1.
A typical diesel engine will have a compression ratio of 22:1. Compare that to a gasoline engine – which usually has a compression ratio of 8:1. That’s almost a 3x increase in compression.
Best compression ratio for a motorcycle

Almost all motorcycles use gasoline engines in them.
Also, no motorcycles use diesel engines. As for why diesel engines are not used in motorcycles, there is a long list of reasons.
If you are interested to know in detail, You can check out our post here on why diesel engines are not preferred in motorcycles.
Back to the topic, gasoline engines are what is used in motorcycles.
So, the optimum compression ratio for motorcycle engines is between 8:1 to 13:1.
This is the compression ratio used in gasoline engines of automobiles. If the compression ratio is lower than optimum, there will be trouble in fuel combustion.
If the compression ratio is too much, like that of diesel engines, then there will be engine knocking.
That’s why it is essential for motorcycle gasoline engines to have their compression ratios in the desired optimum range.
To Summarize
The compression ratio is measured as the volume of the combustion chamber when the piston is at its lowest point (BDC – Bottom dead center) to when the volume when the piston is at its highest point (TDC – Top dead center).
In other words, the compression ratio measures the cylinder volume when the piston is at BDC to the volume when the piston is at BDC.
The compression ratios of gasoline engines used in automobiles are usually between 8:1 to 13:1.
On the other hand, the compression ratios of diesel engines range between 14:1 to 23:1.
Since motorcycles use gasoline engines in them, the optimum compression ratio is between 8:1 to 13:1.
