A spark plug produces electric sparks to ignite the engine.
It draws a high-voltage current to generate that spark. And it draws electricity regularly. So it’s time to look into that electricity flow.
Does a spark plug use AC or DC?
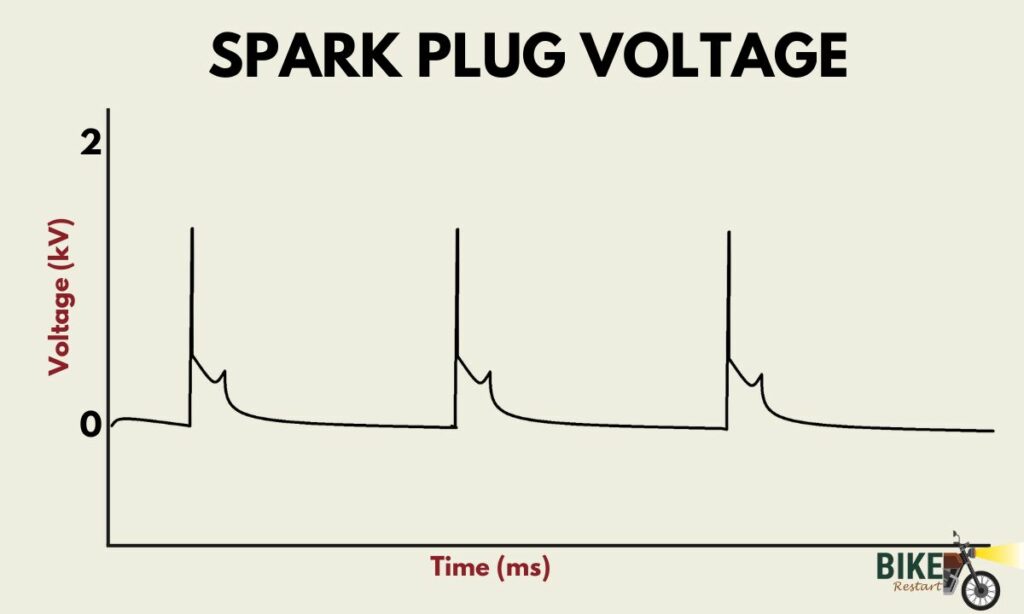
The spark plug uses a high-voltage pulse to generate sparks and ignite the engine. This high-voltage current supply is also called pulsed DC. But a simple pulse is the better term.
And what voltage is used in the spark plug? Usually, the high-voltage electricity in the spark plug will be around 15,000 to 20,000 volts. In modern spark plugs, the voltage can be as high as 60,000 volts depending on the design and the model.
While the answer may seem straightforward, there are lots of nuances that are missed here. Let’s dig deep to understand how the electricity flows in the spark plug.
A Spark Plug Draws AC or DC?
Spark plugs receive high voltage pulse from the ignition coil. This high-voltage current supply can also be called pulsed DC.
So, in a way, you can say the spark plug draws DC. But a high-voltage pulse is a more accurate way to put it.
Here’s how the current supply in the spark plug looks like:
The source of the power is either the battery or from the alternator passed through the CDI unit.
But the electricity flow is not that straightforward though. The current from the alternator or the battery’s DC is of low voltage (usually 12 volts). And spark plugs require around 15,000 to 20,000 volt current to ignite the engine.
So, how does a spark plug get such high voltage? Let’s discuss in the next section.
As for the question: does the spark plug use DC or AC? A spark plug uses a high-voltage pulse. You can call it pulsed DC. But a pulse (without any suffix) is what I would call.
The Flow of Electricity in Spark Plugs
The current flows from the battery or the alternator to the CDI unit, to the ignition coil to the distributor, and finally to the spark plug.
As for how? Let’s dig in.
#1. Power source: Battery or Alternator
The current flow starts from the source – the battery or directly from the alternator.
The current is supplied either by the battery or directly by the alternator passing through the CDI unit.
The current from these power sources then flows to the ignition coil.
#2. Transformer: Ignition Coil
The ignition coil acts as a transformer and uses the low-voltage current supplied to generate high-voltage pulses.

The ignition coil is an induction coil.
This coil transforms the battery’s low voltage, direct current supply into a high voltage supply needed to create an electric spark.
This electric spark in the spark plug finally ignites the fuel.
That’s why, the ignition coil (or the induction coil, whatever you prefer to call it) is essentially a high-voltage transformer.
This transformer has two coils of wire. The primary coil and the secondary coil. Let’s get a bit technical here and understand it’s working.
The two coils are both wrapped within the transformer.
The primary coil is usually the outer coil with a larger diameter whereas the secondary coil is wrapped at a lower radius typically around a rod. Also, the secondary coil has hundreds of more turns of wire than the primary.
The direct current from the battery flows from the battery terminals to the primary coil. This current flow in the primary coil is controlled by the breaker points or a solid-state device depending on the electronic ignition system.
So, when the current in the primary coil is broken by the breaker points, the magnetic field of the primary coil collapses.
As a result, the secondary coil is engulfed in a changing powerful magnetic field. This induces a current in the secondary coil.
Hey, that sounds like electromagnetic induction. You bet it is.
This induced current in the secondary coil is a high voltage current due to the high number of wire windings in the secondary coil. That’s how a high voltage pulse is generated for the spark plug ignition.
Next, this high-voltage current is passed onto the distributor through insulated high-voltage wires. The distributor then passes the high voltage to the appropriate spark plug.
Phew, that’s a long explanation!
Let me try a short and confusing one.
So, in short, the low-voltage current supply is transformed into a high-voltage pulse in the ignition coil.
This high voltage pulse is passed from the coil to the distributor which then passes on to the spark plugs.
#3. Spark in the spark plug
The high voltage pulse from the ignition coil flows through the distributor and finally to the spark plug.
And that high-voltage pulse generates the spark in the spark plug.

At what frequency does the spark plug get this pulse though?
There is another coil called the pickup coil. The pickup coil gives the signal to the CDI unit based on the flywheel rotation.
Based on the pickup coil signal, the high-voltage pulse is transmitted to the spark plug.
What Voltage Does a Spark Plug Need?
Typically, a spark plug needs a high voltage of 15,000 to 20,000 volts to generate the electric spark in the engine.
In modern spark plugs, the voltage can be as high as 60,000 volts depending on the design, spark plug type, and vehicle model.
The high voltage requirement changes based on the vehicle used as well as the spark plug types – copper, platinum, double platinum or iridium spark plug.
Modern automotive spark plugs generate a far higher voltage spark than the old ones. The old spark plugs operated with a voltage of 10,000 volts. Modern spark plugs operate as high a voltage as 60,000 volts.
High-voltage sparks are great
A high-voltage spark has its advantages. Simply put, a high-voltage spark allows for a more energetic and complete ignition. The sparks generated are hotter, larger, and longer lasting.
One of the main reasons modern spark plugs can operate at such high voltage is the improvements on the insulator part of the spark plug.
Two major technological improvements to the insulator include i) using sintered alumina as the insulating material; ii) the addition of ribs to the insulator.
Sintered alumina has good thermal properties as well and can withstand high temperatures. The addition of ribs improved the electrical insulation further.
These technological improvements have resulted in modern spark plugs generating high voltage sparks (as high as 45,000 to 60,000 volts) in engines.
Can a Spark Plug Work Without the Battery?
Since the battery is the power source for the spark plugs in modern automobiles, a spark plug will NOT work without a battery.
Sure the alternator can still make the spark plug work.
But without the engine running, the alternator ain’t generating any current.
You first need the battery to start the engine.
Without the battery functioning in a motorcycle or even in a car, almost all the accessories, circuits, and electronic systems will not work at all.
Forget spark plugs, without the battery, the motorcycle will not even start!
So, yeah. A battery is essential for the spark plug to work. And without the battery, the spark plug will not receive its high voltage current to ignite the spark in the engine.
To Summarize
Spark plugs receive high voltage current from the ignition coil, which uses the battery or the alternator as its power supply.
But, the battery is of 12V and the spark plug needs a high voltage in the range of 15,000V to 20,000V.
And that’s where the ignition coil (also called induction coil) fits in.
The ignition coil acts as a transformer and uses the low voltage current from the battery to convert it to high voltage pulses and pass it onto the spark plugs via a distributor.
Essentially, the low-voltage current supply from the battery is transformed into a high-voltage pulse in the ignition coil. This high voltage pulse is passed from the coil to the distributor which is then passed on to the spark plugs for spark ignition in the engine.
Typically, a spark plug needs a high voltage of 15,000 to 20,000 volts to generate the electric spark in the engine.
Before you go…
Here are a few more spark-plug posts for you:
