This is a complete guide to motorcycle spark plugs.
In this new guide, you’ll know everything about spark plugs, including:
- Spark plug functions
- Components
- Different types
- Spark plug gap
- Deposits
- How to know if the spark plug is bad and when to change
- And all other spark plug details
Let’s jump right in.
Spark plug’s function in an engine
A spark plug is the component used to ignite the fuel mixture in gasoline engines.
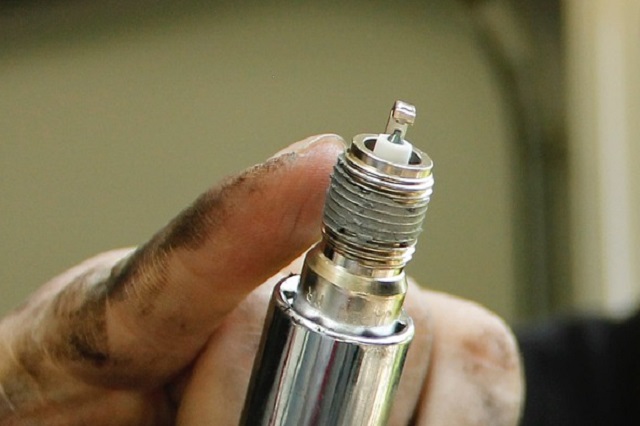

The spark plug ignites the fuel by producing a high-voltage spark in the combustion chamber. The spark generated ignites the gasoline mixture. Paving for the fuel combustion.
The spark produced will be in the range of 15,000-20,000 volts.
Without a spark plug, the fuel mixture in the engine will not combust at all.
No spark ignition. No fuel combustion. Hence, no power is generated by the engine. That’s why a spark plug is such an essential component for a motorcycle.
Spark plug components
Let’s briefly look into spark plug parts and their roles.
Terminal
The terminal connects the distributor cap from the ignition system to the center electrode. The high-voltage electricity is conducted by the terminal right to the central electrode.
In short, the terminal acts as the connector to pass the high-voltage electricity to the center electrode.
Insulator
The insulator insulates the terminal and the shaft that connects the terminal and the center electrode.
This insulation is crucial to prevent the electricity from flowing away from the electrode. Plus, it ensures the high voltage is not lost while transmitting along the shaft.
Shell
Spark plugs usually have a steel shell to facilitate tightening and loosening of the plug.
The shell also provides electrical ground for the ground electrode and helps in heat transfer via the cylinder head.
Threads
The threads along with the shell ensure that the spark plug is fit tightly on the cylinder head. They cover the insulator and provide support as well.
The main function is of course to help in spark plug installation.
Center Electrode and Ground Electrode
The center electrode is connected to the terminal through a central shaft. The high-voltage electricity is passed from the terminal through the shaft to this center electrode. Usually, the electrode is made of copper alloy, platinum, or iridium depending on the spark plug type.
The ground electrode acts as the grounding for the high-volt electricity in the spark plug. It is a fail-safe to avoid any electrical hazard in the spark plug since it carries away any excess electricity generated.
The center electrode tip carrying the high voltage generates the spark in the small gap between this electrode and the ground electrode.
This spark is what ignites the fuel mixture in the engine.
Motorcycle won’t start without spark plugs
All conventional motorcycles run on gasoline engines. And gasoline engines need spark plugs to keep running. Without a spark plug, a gasoline engine will not even start.
So yes, a motorcycle will not start without a spark plug.
As long as the spark plug is not working, the engine won’t run.
Gasoline engines need, let me be clear, gasoline engines absolutely need spark plugs to ignite the fuel and run.
Types of spark plugs
Spark plugs can be classified based on different parameters.
The most common classifications include: based on the material used for the center electrode; based on the resistance; and based on tip temperature (hot vs cold).
Let’s dive into each of these.
Based on the tip material
Sparks are classified into three main types based on the material used as the center electrode:
- Copper spark plugs
- Platinum spark plugs (single and double)
- Iridium spark plugs
I won’t dive into too much details. I have made a separate long post explaining these 3 types of spark plug materials.
But here is the gist:
Copper spark plugs are the cheapest spark plugs and are widely used. They are still popular but not the best in terms of performance and durability.
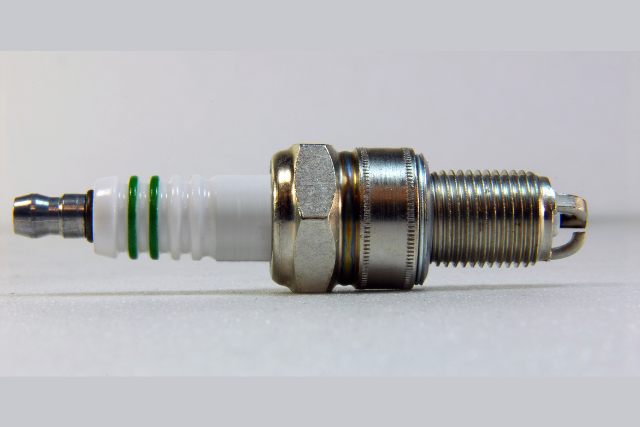
Iridium spark plugs are the best-performance spark plugs in the market right now. But they are expensive.
Platinum spark plugs are somewhere in between these two spark plugs. They act as a compromise between cost and performance.
Based on the resistance
Based on the resistance of the spark plugs, there are two types:
- Resistor spark plugs
- Non-resistor spark plugs
If the spark plug has a resistor in it, it’s a resistor spark plug. If no resistor – non-resistor spark plug.
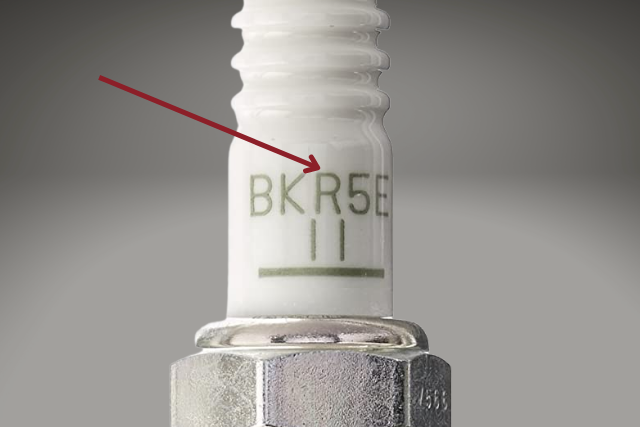

Simple and straightforward eh.
For almost all automobiles, resistor spark plugs are the best option.
Non-resistor spark plugs are only used as racing plugs in racing cars and motorcycles.
For more details, here is our explainer.
Based on heat transfer
Spark plugs are classified into types based on their heat transfer and the tip temperature:
- Hot spark plugs
- Cold spark plugs
Put simply, if the spark plug tip gets too hot and has a very high temperature it’s a hot spark plug. If it is not maintained at a high temperature, it’s a cold spark plug.
The difference is in the design.
Hot spark plugs have more insulation near the tip. The insulation prevents heat transfer and keeps the tip at high temperatures.
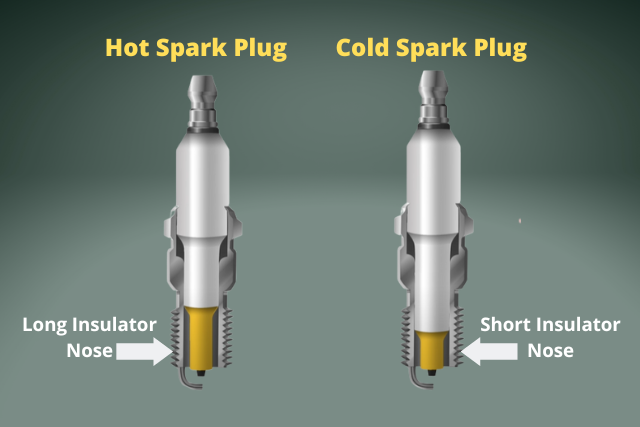
Cold spark plugs have less insulation. So more heat transfer. And the tip is not too hot.
Hot spark plugs are common and are used widely. Especially in low-compression engines. Cold spark plugs are used in high-compression engines like turbo and superchargers.
Spark plug gap
The spark plug gap is the space between the center electrode and the ground electrode in the spark plug.
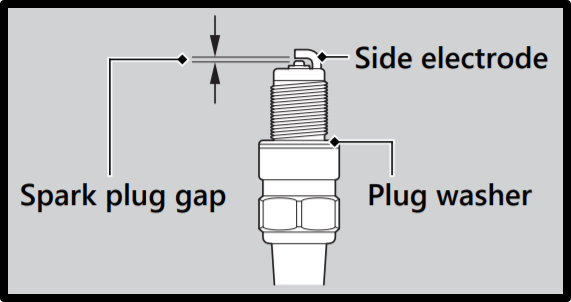
The gap is crucial
The spark plug gap is critical because it influences the electric arcing which is essential for fuel ignition.
The spark plug gap should be right according to the specifications given.
If the spark plug gap is too big, the spark requires more voltage to be transferred from the ignition coil resulting in higher electricity consumption and inefficient ignition.
If the spark plug gap is too small on the other hand, the spark will be weaker and will have less contact with the air-fuel mixture resulting in incomplete combustion. Or even no ignition at all causing engine misfiring.
Is the gap preset?
Most spark plugs come with a preset gap.
However, a preset gap does not mean the right gap. Different engines and applications have different spark plug gap requirements.
Each engine, be it in an automobile – car or motorcycle, or in a piece of machinery and equipment like a lawn mower, works optimally at a certain spark plug gap.
As a result, the preset gap is not the right gap for most engines.
So, most of the time, one has to gap the spark plug again before installing the spark plug.
How to gap
A spark plug can be gapped using any of the tools and methods. The 3 tools widely used for gapping are:
- Coin gauge
- Feeler gauge
- Wire gauge
Coin gauge is the most convenient, and hence, the most popular tool used for spark plug gapping after service.
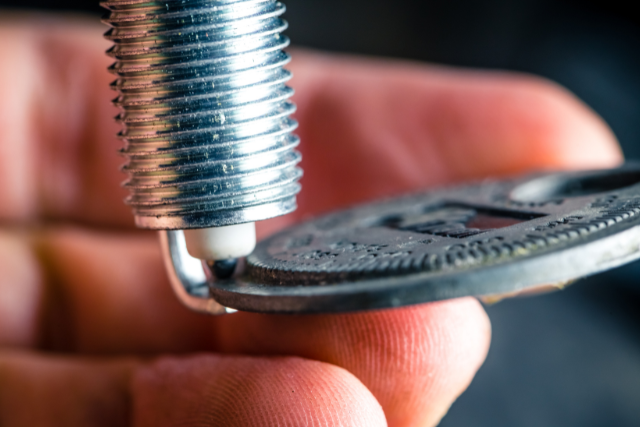

The feeler gauge is simple but you need other tools to widen or reduce the spark plug gap. The feeler gauge in itself is only a gap thickness measurement tool.
Wire gauge is another viable alternative. While the handling is not intuitive unlike the coin gauge or the feeler gauge, they don’t have as many complaints of tip breakage as coin gauges.
Spark plug deposits
Spark plug deposits are common if you have been using the spark plug for quite some time.
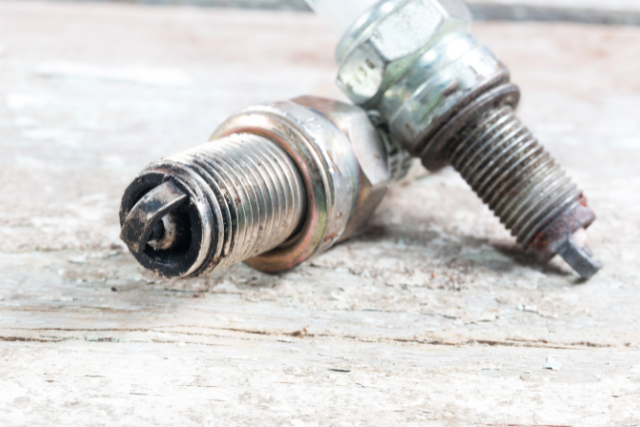

I am gonna keep this short. The long version is here.
Here are the different spark plug characteristics and what they mean for the spark plug:
- Oil fouling: black and wet deposits, greasy in texture.
- Carbon fouling: black and dry deposits, sooty in texture.
- Ash deposits: white crusty deposits, dry and sandy in texture.
- Worn-out spark plug: the center electrode is worn out and can be hardly seen.
- Normal spark plug: no deposits, slight discoloration.
Spark plugs getting damaged
Spark plugs can go bad for numerous reasons. Identifying that the spark plug is damaged can get quite tough.
So let’s look into the causes, symptoms, and tests (how to confirm) when a spark plug is damaged.
Causes
There are several reasons for the spark plug to go bad. The main reasons fo failure are:
- Too rich a fuel mixture
- Engine oil leak
- Coolant leak
- Cracked distributor case
- Dirty fuel injector, carburetor, or air filter
- Incorrect heat range or wrong spark plug
- Improper plug gapping
We go into detail about these causes here. But yeah, for now, the list should suffice. Else the post is gonna be too long (It’s already too long :/).
Symptoms
Bad spark plugs are a bit difficult to trace. But here are the seven definite symptoms of bad spark plugs that you should be aware of:
- Motorcycle is hard to start
- Engine misfiring
- Low fuel economy
- Rattling engine noise
- Lack of power
- Reduced acceleration
- Rough idling
How to test
How to know for sure the spark is bad then?
You can test the spark plug. It won’t take much time.
Test #1: Check the center electrode and spark plug deposits
If the center electrode is worn out or has deposits (oil foul, carbon deposits, or ash deposits), then the spark plug is bad. Replace it.
Test #2: Check the resistance between the terminal and the tip
Take a multimeter. Check the resistance between the terminal and the tip of the center electrode.
For non-resistance spark plugs, the resistance reading should be almost zero. For resistance spark plugs, the resistance reading typically will be between 4000 ohms to 6000 ohms.
If the resistance is higher than the above-mentioned ohms, the spark plug must be replaced.
Test #3: Check the resistance between the two electrodes
Use the multimeter to measure the resistance between the center and ground electrodes.
There should be no conductivity as these two electrodes must be isolated from each other.
Check the resistance between the terminal (center electrode) and the threads (ground electrode).
Check the multimeter reading. It should not move an inch.
If the resistance reading is not nil, then you must discard the spark plug.
When to change spark plugs
A motorcycle spark plug lasts around 10,000 miles (16,000 kilometers). Platinum and Iridium spark plugs last much longer.
For conventional copper spark plugs, you should replace them every 8000 miles to 10,000 miles.
In addition, you should check the spark plug condition every 4000 to 5000 miles.
Spark plugs vs Glow plugs
Spark plugs are the components used to ignite the fuel mixture in gasoline engines. Whereas glow plugs are electrical heating components fitted in diesel engines.
They are completely different components.
One is used in gasoline engines to ignite the fuel mixture. The other is used in diesel engines to preheat the chamber.
You can find the detailed differences laid out here.
But here is a cool infographic from me giving you the gist.
Other spark plug details
Now that we have covered the main aspects, let’s dig into the miscellaneous parts.
Weight
A spark plug’s weight typically ranges between 25 to 60 grams (0.88 to 2.12 ounces).
The average weight of spark plugs used in automobiles will be around 45 grams (1.59 ounces).
We tested the weight of 12 spark plugs to arrive at this average figure. Although by no means this is a comprehensive study, we believe this gives a fair idea of what an average spark plug weight is.
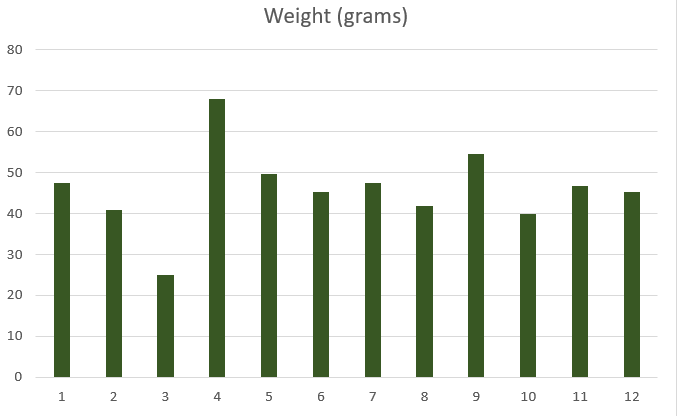
The exact mean weight of the spark plug was 46.01 grams (1.62 ounces) and the median was 46.07 grams (1.62 ounces).
What was more interesting in this small sample study is the lack of correlation with the type of spark plug.
Again, we understand the lack of correlation might have also to do with the limited sample size we had for this study. Still, from our observation, we believe the type of center electrode used material has little impact on the spark plug weight.
Cost
A typical spark plug costs less than $10 with a copper spark plug available at just $2.5.
Platinum and iridium spark plugs are costlier than copper spark plugs. Still, you can easily get them for around $5 to $12.
Iridium spark plugs are available at even high prices though depending on your desired specifications. However, even the best iridium spark plugs for automobiles should be available for less than $15.
If you are buying a set of spark plugs, then a set of 4 or 6 spark plugs should be in the price range of $10 to $60. The price depends on the spark plug type and how many plugs are there in a set (usually it is 4 or 6).
The replacement cost for a motorcycle spark plug costs around $60 including parts and labor charges.
Voltage requirements
Spark plugs require a high-voltage current to ignite the engine. The voltage requirement is around 15,000 to 20,000 volts.
The current is supplied either by the battery or directly by the alternator passing through the CDI unit. Both as DC.
Either way, the current goes through the ignition coil which acts as a transformer. The ignition coil converts the low-voltage current to high-voltage pulses and passes them onto the spark plugs.
Heat range
The optimum spark plug temperature range is between 500 to 800 degrees Celsius (or between 900 to 1500 degrees Fahrenheit).
By spark plug temperature, we are referring here to the center electrode temperature. This is where the spark originates.
Again, the operating temperature can vary based on the electrode material, engine conditions, insulator, and the spark plug type (hot vs cold).
If the spark plug is operating at a temperature below the optimum range, then you will start noticing carbon deposits. The low electrode temperature allows the unburnt fuel to start depositing.
If, on the other hand, the spark plug temperature is too high, there will be pre-detonation. The air-fuel mixture will start burning even before the spark ignition.
Who invented the spark plug
The first documented spark plug use was by Jean Joseph Étienne Lenoir in 1859.
So, Étienne Lenoir is attributed as the inventor of spark plugs.
The basic spark plug design was further refined and evolved over time.
The most notable spark plug designs and patents were by:
- Nikola Tesla
- Frederick Richard Simms
- Robert Bosch
While Tesla, as well as Simms, furthered the spark plug design, it was Bosch’s patent (in 1902) that eventually developed into a commercial spark plug.
Robert Bosch was the first-ever company to develop a commercially viable spark plug.
Over the century, the spark plug has seen numerous refinements and modifications. To know more, here is a brief history of spark plugs.
Final words
This was a long post. I have tried my best to cover the entirety of the spark plugs. It could have been even more long. But I have kept things concise and have linked relevant posts (within each section) for further reading.
Still. I hope you loved this long-ass article. Let me know what you think of it in the comments.
