Resistor and non-resistor spark plugs are differentiated by a resistor. And that changes a lot of things in how they function.
So first, what are resistor and non-resistor spark plugs? Resistor spark plugs are those spark plugs that have a resistor in their center electrodes. Non-resistor spark plugs, on the other hand, do not have any resistor on their center electrodes.
Okay.
Which is better then? Resistor or non-resistor spark plugs? For almost all automobiles, resistor spark plugs are the best option. Non-resistor spark plugs are only used as racing plugs in racing cars and motorcycles.
Now that we have an idea about these spark plug types, let’s dig in deeper.
What Are Resistor and Non-Resistor Spark Plugs

Resistor spark plugs are those spark plugs that have a resistor in their center electrodes.
Non-resistor spark plugs, on the other hand, do not have any resistor on their center electrodes.
The resistor in the center electrode is what differentiates a resistor spark plug from a non-resistor spark plug.
That’s it. That’s the main difference. If there is a resistor, it’s a resistor spark plug. If not, then it’s a non-resistor spark plug.
Earlier spark plugs were all non-resistor spark plugs. Up until the 1960s, all automobiles used non-resistor spark plugs. Resistor spark plugs were not even on the market.
But, a major downside of non-resistor spark plugs is that their spark produces a high frequency of energy resulting in electromagnetic interference. And most notably radio frequency interference (RFI).
The radio frequency interference caused several problems with the electronic pieces of equipment installed in the vehicles.
And that’s how, to overcome this problem, resistor spark plugs were developed.
Resistor spark plugs were developed in the 1960s with a resistor added to the center electrode. These spark plugs suppressed the spark energy and in effect, reduced the electromagnetic and radio frequency interference.
If you are interested, here is a post on spark plug history.
So that’s how resistor spark plugs were born. Nowadays, resistor spark plugs are the widely used spark plugs. Non-resistor spark plugs are only used in niche applications and mostly as racing plugs.
How To Identify?
Now, how do you identify whether the spark plug is a resistor type or a non-resistor type by looking at the spark plug?
Well, there is a way.
Usually, the resistor spark plugs have an “R” in their model names. If you look at the insulator where the model name is inscribed and you see an “R”, then that is a resistor-type spark plug.
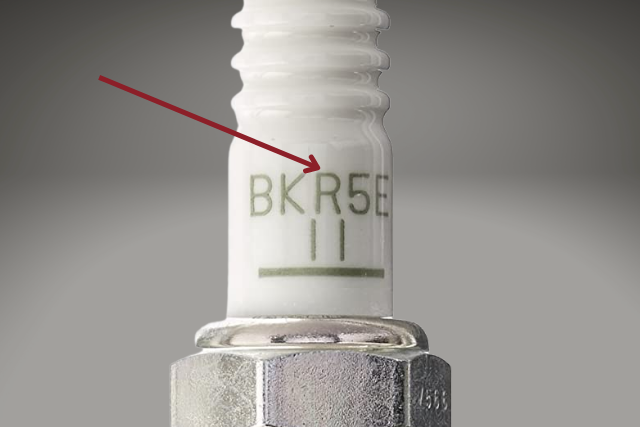

On the other hand, non-resistor spark plugs do NOT contain an “R” in their model names.
This is of course by design to ensure an easy differentiation between a resistor and a non-resistor spark plug. I would be really surprised to see an “R” in a non-resistor spark plug model name.
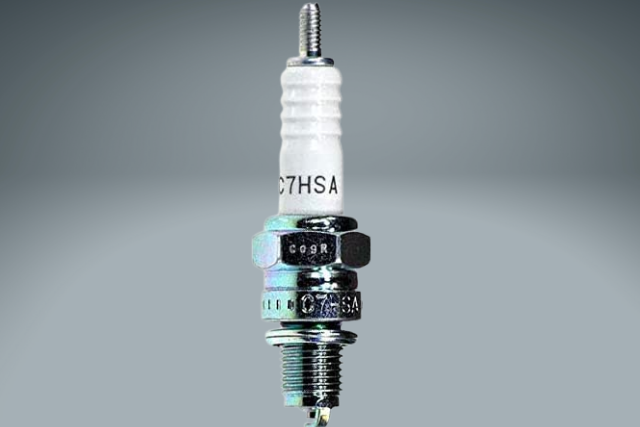

And that’s how you can easily identify whether the spark plug is a resistor type or non-resistor type.
Of course, this is not a mandatory rule but rather a thumb rule. Manufacturers can go ahead and not follow this rule. But generally, it is considered a good practice and manufacturers do practice this.
Resistor Spark Plug Features
Resistor spark plugs, as discussed above, have a resistor in their center electrodes.
The main purpose of introducing center electrodes is to reduce the frequency of energy produced by the spark. This helps in lessening the electromagnetic and radio frequency interference by the spark plug.
When resistor spark plugs were introduced in the 1960s, the reduced electromagnetic interference came at a cost. This is low intensity and less powered sparks.
Typically, the resistor in the center electrode of a resistor spark plug will be around 4000 to 6000 ohms.
To check the spark plug resistance, you can use a multimeter and measure the ohm reading by placing the leads on the terminal and the tip.
Resistor spark plugs produce slightly weaker sparks when compared to non-resistor spark plugs.
However, this is no longer a concern. Modern ignition systems and high voltage sparks have ensured that the resistor spark plugs, in fact, produce moderately strong sparks sufficient for engine combustion.
As a result, resistor spark plugs are widely popular and are used in almost all automobiles.
Pros:
- Reduced electromagnetic interference
- Reduced radio frequency interference
- Low noise
Cons:
- Low-intensity sparks (which are no longer a concern since they are strong enough for modern engine ignition).
Non-Resistor Spark Plug Features

Non-resistor spark plugs do not have a resistor in their center electrodes.
They were the only type of electrodes available on the market before resistor spark plugs were developed in the 1960s.
The main problems of non-resistor spark plugs were that the high-frequency energy of the sparks paved way for electromagnetic and radio frequency interference.
This led to the electronic pieces of equipment installed in the vehicle facing noise and disruptions. That’s the reason resistor spark plugs were developed.
Still, non-resistor spark plugs have an advantage over resistor spark plugs when it comes to the intensity of the sparks produced. Non-resistor spark plugs produce far stronger sparks when compared to resistor spark plugs.
Pros:
- Strong and high-powered sparks
Cons:
- High noise
- Electromagnetic and radio frequency interference
Key Differences
The key differences between a resistor spark plug and a non-resistor spark plug are tabulated below:
| Parameter | Resistor Spark Plug | Non-Resistor Spark Plug |
|---|---|---|
| Difference | Has a resistor in the center electrode | No resistor in the center electrode |
| How to identify | The model name has “R” in it | No “R” in the model name |
| Spark Intensity | Moderately strong | Strong and high powered |
| Noise and Electromagnetic interference | Low | High |
| Used in | Almost all Automotives | Racing cars and motorcycles |
Here is a highlighting infographic for resistor vs non-resistor spark plugs:
Which Is Better? Resistor or Non-Resistor Spark Plugs

The million-dollar question. Which spark plug type is better? Resistor spark plugs or non-resistor spark plugs?
For almost all vehicles – be it cars or motorcycles, and even automotive like lawn movers, resistor spark plugs are the best option.
This is because resistor spark plugs have low electromagnetic and radio frequency interference. This helps in the smooth functioning of other electronic equipment installed in the vehicle.
So, if you are confused about which spark plug type to go for – go with the resistor spark plug type.
Non-resistor spark plug type, although not a great fit for modern engines, does have its fans. They are exclusively used nowadays as racing plugs.
For racing cars and motorcycles, non-resistor spark plugs are preferred owing to their high-powered and strong sparks.
Conclusion
Resistor spark plugs have a resistor in their center electrodes. And non-resistor spark plugs do not have a resistor in their center electrodes.
Usually, the resistor spark plugs have an “R” in their model names. If you look at the insulator where the model name is inscribed and you see an “R”, then that is a resistor-type spark plug.
The main purpose of introducing center electrodes is to reduce the frequency of energy produced by the spark. This helps in lessening the electromagnetic and radio frequency interference by the spark plug.
That’s why, for almost all automobiles, resistor spark plugs are the best option.
Non-resistor spark plugs are only used as racing plugs in racing cars and motorcycles.
